-
Our offer is only for you if you are of legal age. Please confirm that you are at least 18 years old to proceed.
Our offer is only for you if you are of legal age. Please confirm that you are at least 18 years old to proceed.
Last updated on 29/04/2025 | Reading time approx. 02:53 min

If you've always wondered how a hookah works – how it's possible to smoke shisha tobacco through a water-filled glass base – you're in the right place. In this article, we’ll walk you through the individual components of a hookah and provide all the essential information you need to understand the basic principle that applies to pretty much every hookah. To do that, it's important to know the individual parts of a hookah:
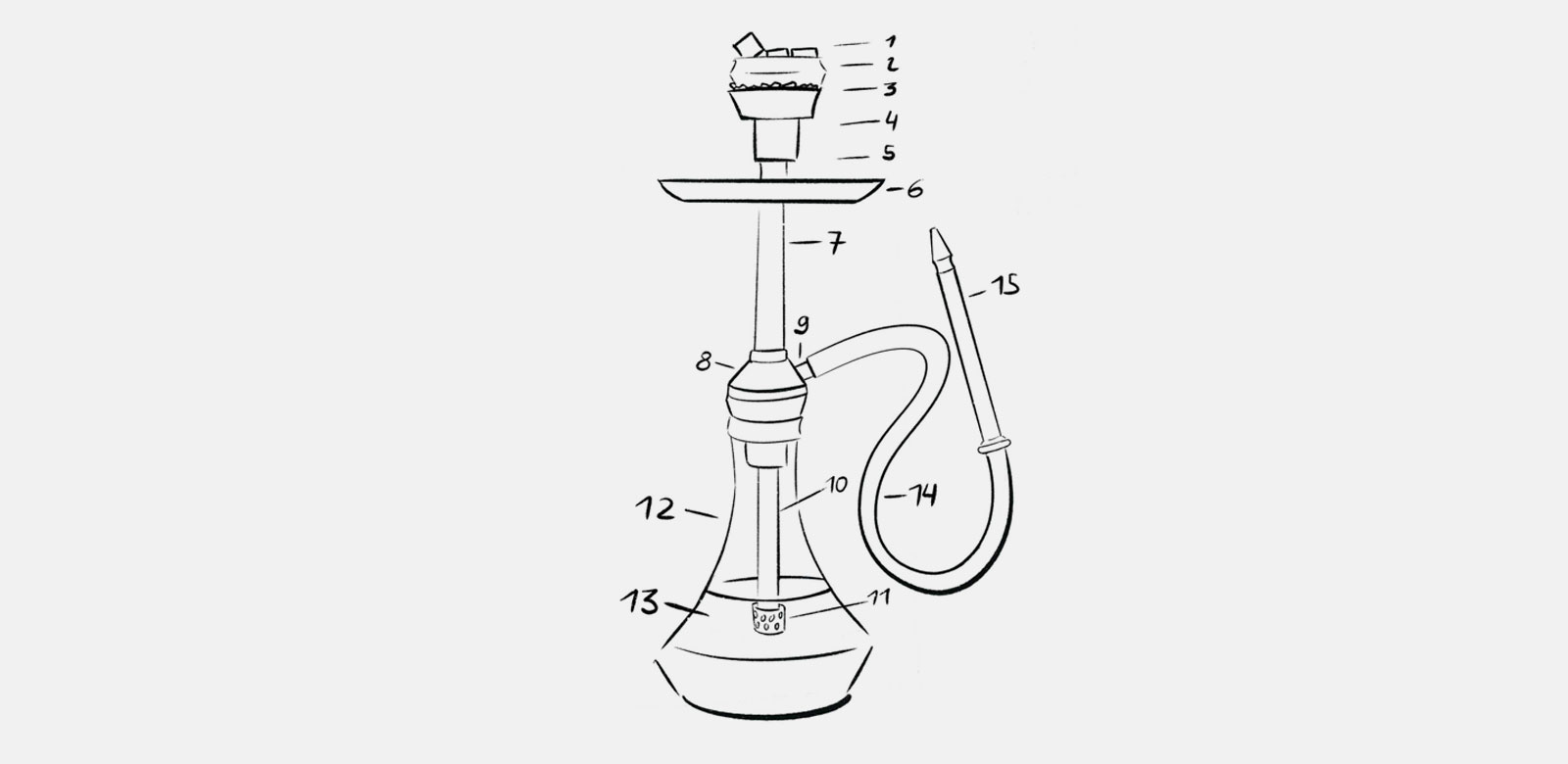
1. Charcoal / 2. HMD / Foil / 3. Tobacco / 4. Bowl / 5. Bowl adapter / 6. Charcoal tray / 7. Smoke column / 8. Base / 9. Hose connector / 10. Downstem / 11. Diffuser (optional) / 12. Glass base / 13. Water / 14. Hose / 15. Mouthpiece
Let’s assume your hookah is already set up and ready for a session.
There’s water in the glass base, your bowl is filled with your favorite tobacco, and the charcoal has been lit and placed in the HMD, so you're good to go.
You grab the mouthpiece, place it to your lips, and take a deep pull. As you inhale, air is drawn through the hookah hose out of the glass base. This creates a vacuum inside the base.
If your hookah were made of very thin material, it would collapse at this point. But since that's not the case, the vacuum is equalized by drawing in air from the next weakest point – which in this case is the air inside the downstem submerged in water. As this isn't enough to compensate for the vacuum and the missing air in the downstem also needs to be replaced, fresh air is drawn in from outside the hookah.
This fresh air now flows past the charcoal, heating it up even more. The charcoal then heats the tobacco, causing part of the molasses and the flavors in the tobacco to evaporate. This produces smoke and even more heat.
The hot smoke then travels down the smoke column and into the water of the glass base. There, it is cooled and creates the iconic bubbling sound of a hookah as it rises through the water.
Next, the smoke flows through the base, along the hose, and ends up exactly where the vacuum was created – in your lungs. That’s basically it. Almost every hookah on the market operates on this same principle. Blow-off systems, however, work a little differently.
Unlike regular smoking, blow-off systems function a bit differently. With a blow-off, the smoke no longer needs to be cooled, meaning it doesn’t have to be pushed back through the water.
Instead, you exhale the drawn-in smoke directly through dedicated outlets in the base.
These outlets usually contain small balls. When you inhale, these balls are sucked into place to block fresh air from entering through the exhaust ports. During the blow-off, however, the pressure in the glass base increases, pushing the balls up and allowing the smoke to escape through the designated blow-off outlets – depending on the design of the hookah.

The difference between smoking and blow-off
Some hookahs even feature a variable blow-off system, which can be adjusted between sessions – or even during the session – with just a few simple steps.
We hope we’ve answered all your questions! We’re always happy to receive your feedback. And of course, you’ll find a wide selection of hookahs in our shop.
Visit Our Hookah ShopBeim Ziehen am Mundstück entsteht ein Unterdruck in der Bowl. Dadurch wird Luft von außen durch die Kohle gezogen. Diese erhitzt den Tabak, wodurch Rauch entsteht. Der Rauch wandert durch das Wasser in der Bowl, wird abgekühlt und gelangt dann über den Schlauch zu dir.
Eine typische Shisha besteht aus folgenden Bauteilen:
• Kohle
• HMD oder Alufolie
• Tabak
• Kopf & Kopfadapter
• Kohleteller
• Rauchsäule
• Base
• Schlauchanschluss
• Tauchrohr
• Diffusor (optional)
• Bowl mit Wasser
• Schlauch
• Mundstück
Nein. Der Tabak wird nicht verbrannt, sondern durch die Hitze der Kohle langsam erhitzt. Dabei verdampfen Molasse und Aromen – es handelt sich um ein Schwelprozess, nicht um eine Verbrennung.
Ein Diffusor sorgt dafür, dass das Blubbergeräusch beim Rauchen deutlich leiser wird. Das ist sehr praktisch, wenn man neben dem Rauchen zum Beispiel Videos schauen möchte oder wenn die Wohnung hellhörig ist.
Beim Blow-Off wird Rauch aktiv aus der Bowl durch dafür vorgesehene Öffnungen ausgeblasen. Kleine Kugeln in diesen Auslässen heben sich durch den Überdruck und lassen den Rauch austreten. Je nach Shisha-Design kann ein Blow-Off sehr unterschiedlich gestaltet sein.
Nein! Variable Blow-Off-Systeme waren eine Zeit lang sehr gefragt und haben immer noch ihren Platz in der Community. Bei uns findest du zum Beispiel die Moze Breeze Two, die Moze Breeze Pro und die Moze Varity, die dieses Feature bieten. Die Breeze Two stand damals sogar im Zentrum des Hypes rund um den variablen Blow-Off.
Ja, obwohl das Grundprinzip bei allen gleich ist. Unterschiede gibt es vor allem im Design, bei den Blow-Offs, beim verwendeten Material und beim Zubehör – und genau diese Details beeinflussen das Rauchverhalten deutlich.
