-
Our offer is only for you if you are of legal age. Please confirm that you are at least 18 years old to proceed.
Our offer is only for you if you are of legal age. Please confirm that you are at least 18 years old to proceed.
Author

Last updated on 28.08.2025 | Reading time approx. 5:30 min

Vapes are electronic devices that vaporize liquids instead of burning tobacco. This guide summarizes all important information about how they work, differences from e-cigarettes, health risks, legal aspects, and proper disposal.
What to expect here
What are vapes? Difference: Vape and E-cigarette Since when have vapes existed? How do vapes work? How harmful are vapes? Are nicotine-free vapes harmful? From what age can you buy vapes? Can you take vapes on a plane? Disposing of vapes: How to do it right FAQs about vaping Conclusion: What you should know about vapesVapes – also known as e-cigarettes, e-hookahs, or e-vaporizers – are electronic devices that heat a flavored liquid (e-liquid), producing an inhalable vapor. These liquids consist of various ingredients such as propylene glycol, glycerin, nicotine, and a wide variety of flavors. The flavors originally come from the food industry and are specifically adapted by manufacturers for use in e-cigarettes. There is a wide range of flavors – including menthol, mint, or cinnamon – which are particularly popular among young people. Cartridges (known as pods) serve as refills for liquids and are used in many devices. Unlike traditional cigarettes, vapes do not involve combustion. This makes them an interesting alternative to conventional cigarettes for many smokers.
Features:

Vaping with pod systems or tanks
In everyday language, the terms “vape” and “e-cigarette” are often used synonymously. Both refer to the same principle: vaporization instead of combustion. However, the term “vape” comes from the English “to vaporize” and can also refer to other devices that vaporize liquids or substances – for example, inhalation devices for bronchial diseases or devices that vaporize plant material or solid substances for inhalation.
Here in a table for better overview:
| Feature | Vape (colloquial) | E-cigarette (technically correct) |
|---|---|---|
| Terminology | Everyday term | Technical term |
| Device types | Disposable, pod systems, mods | Mainly pod or mod systems |
| Focus | Lifestyle & convenience | Functionality |
| Target audience | Younger demographic | Specialist trade / professional exchange |
| Nicotine content & limits | Often liquids with various nicotine strengths, maximum allowed: 20 mg nicotine per ml according to legal regulation | Strict compliance with the legal maximum of 20 mg nicotine per ml; sizes and ingredients subject to regulatory standards |
First market-ready models: around 2003 (China)
EU-wide spread: from around 2008
Boom in Germany: since around 2015
The history of vapes shows how these products have continuously developed and established themselves on the market since their launch in 2003. In particular, market dynamics and the increasing availability of e-cigarettes have significantly contributed to their widespread use today.
E-cigarettes always consist of five main components:
How vapes work:
The battery supplies power and contains a cell that serves as the central energy source. The battery is not only crucial for functionality but also poses an environmental issue when disposing of disposable vapes.
The coil heats up due to the electrical current.
When heating the liquid, chemical interactions between the ingredients can occur, potentially creating harmful by-products. The liquid vaporizes.
The user inhales the vapor.
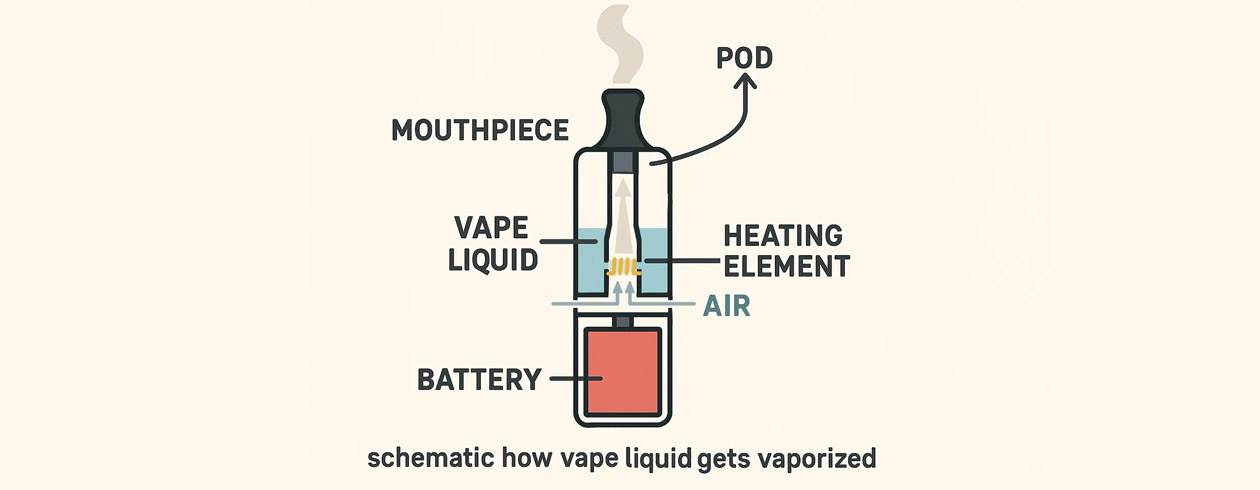
Diagram: Liquid → Vapor
Vapes are often advertised as a less harmful alternative to tobacco products such as cigarettes. In fact, significantly fewer harmful substances are produced when vaping, since there is no combustion. Nevertheless, vapes are by no means risk-free: Especially for young people and non-smokers, consumption carries potential dangers – such as the development of nicotine addiction or acute nicotine poisoning (“nicotine shock”) if overdosed. Studies also show that certain ingredients in liquids can release harmful substances at high temperatures.
Comparison: Vape vs. conventional (tobacco) cigarettes
| Criterion | Vape | Tobacco cigarette |
|---|---|---|
| Tar | ❌ Not present | ✅ Present |
| Combustion | ❌ No combustion | ✅ Yes |
| Amount of harmful substances | 🚫 Significantly lower | 🔥 High |
| Odor nuisance | ❌ Minimal | ✅ Strong |
| Nicotine (optional) | ✅ Optional | ✅ Always included |
Note: Vapes are considered less harmful in comparison – but are not risk-free. The long-term effects have not yet been fully researched. Consumption is particularly discouraged for non-smokers or young people, but for regular smokers, they can be an alternative or make quitting easier.
Nicotine-free vapes can also pose health risks. While the addictive substance nicotine is absent, the liquids often contain flavorings whose inhalation may be problematic. Studies suggest possible respiratory irritation as well as allergic reactions. As research is not yet complete, caution is advised when consuming. Conclusion: Even though vapes are considered less harmful compared to traditional cigarettes, they are by no means harmless. Young people in particular should be aware of the possible risks and, considering that consumption is only permitted from the age of 18, should not expose themselves to these concerning substances. For smokers who want to quit tobacco, the e-cigarette can be a useful intermediate step – provided it is used responsibly.
In Germany: from 18 years old
Also applies to nicotine-free e-cigarettes and liquids
Sale to minors is prohibited by law
Online retailers are obliged to carry out age verification
Info: In many other countries, similar age restrictions apply to the purchase and consumption of vapes.
When traveling or ordering online, you should always check the local legal regulations.
| Aspect | Allowed? | Note |
|---|---|---|
| Device in hand luggage | ✅ Yes | Must be switched off |
| Liquid in hand luggage | ✅ Max. 100 ml per bottle | In 1-liter bag, max. 10 liquids |
| Use on the plane | ❌ No | Strictly prohibited |
Tip: Also check with your airline for current guidelines. Some airports also prohibit vaping inside terminals.
🔄 Where does what go?
| Component | Disposal |
|---|---|
| Disposable vape | Recycling center / e-waste collection point |
| Battery (built-in) | Also e-waste |
| Liquid residue | Household waste (in small amounts, tightly sealed) |
| Packaging | Yellow bag / recycling |
⚠️ Important: Never throw batteries/devices with batteries into residual waste – risk of fire & environmental hazard! Even small devices contain lithium-ion batteries.
Studies suggest that e-cigarette consumption can impair vascular function. Particularly in young adults (e.g., ages 17 to 25), there are early indications of effects on the cardiovascular system. Even though the effects are lower compared to traditional smoking, a health risk remains.
Disposable e-cigarettes often contain highly concentrated amounts of nicotine and are particularly popular among young people. Due to their easy availability and relatively low price, they are a common entry point – which increases addiction potential. They also cause environmental issues, as they are often not disposed of properly.
E-cigarette vapor contains, in addition to propylene glycol and glycerin, flavorings and possibly nicotine. Studies have also detected traces of metals, acetaldehyde, and formaldehyde. These substances usually result from overheating of the coil or the use of low-quality materials.
In Germany, there is currently no complete ban on vapes, but such a measure is being intensively discussed in the context of youth protection and sustainability. Some countries, such as France, have already announced a future ban. International position papers from professional societies also support such a ban.
Vaping is considered a modern lifestyle. The stylish devices, sweet flavors, and strong presence on social media make e-cigarettes particularly attractive to young consumers. However, this leads to a dangerous misconception: Many underestimate the health risks – especially compared to traditional cigarettes.
Vaporizers are devices that usually gently heat herbs, plant material, or solid substances, while e-hookahs and vapes vaporize liquid e-liquid. The taste of e-hookahs is often sweeter and more similar to hookah tobacco, while vapes are more compact and designed for everyday use. All three types carry similar health risks – especially with improper use or regular consumption by young people.
E-liquids consist of so-called base substances such as propylene glycol and vegetable glycerin as well as flavorings and possibly nicotine. According to current studies, potentially harmful substances such as formaldehyde or heavy metals can form under high heat – especially with improper use or low-quality devices.
Author

